Paresis Hindbrain tumors can cause weakness in the limbs. Ocular melanomas are at least in part heritable and caused by one or more genetic mutations.

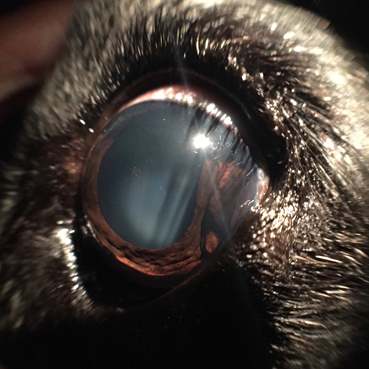
This type of dog eye tumor appears as a reddish pink mass in the eye pupil towards the rear of the iris.
Eye tumor dog. Ocular melanomas although rare are the most common eye tumor in dogs. Ocular melanomas can originate from the uvea or the limbus. About 80 of uveal melanomas and all limbal melanomas are benign.
The rate of metastasis is less than 5. Ocular melanomas are at least in part heritable and caused by one or more genetic mutations. Eyelid tumors are the most frequent group of eye tumors in dogs.
Adenoma a benign tumor and adenocarcinoma a malignant tumor of the meibomian glands in the eyelid are the most common lid tumors. Because these tumors tend to be disfiguring as well as irritating to the dog they are usually surgically removeda process that is usually successful. Eyelid tumors are the most common eye tumors that occur in dogs.
Fortunately the majority of them are benign eg meibomian gland adenomas and papillomas and the dogs face excellent prognosis following either surgical excision or. This type of dog eye tumor appears as a reddish pink mass in the eye pupil towards the rear of the iris. Cilary body neoplasia can trigger glaucoma.
If this dog eye condition can be diagnosed early it can be corrected with surgery. In dogs the second most common eye tumor are ciliary body adenomas and adenocarcinomas melanomas of the eye are the most common and more information can be found in the handout Eye Tumors - Melanoma in Dogs. Other primary intraocular tumors occur but are extremely rare.
One of these is a rare type of spindle cell tumor in dogs known as uveal schwannomas of. Eyelid tumors in dogs are very common especially in older dogs. The majority of these eyelid tumors are non-cancerous but there are some tumors that are cancerous.
Eyelid tumors many times occur on the glands that line the eyelid margins. These tumors generally do not cause your dog any problems they are cosmetic. However if the tumors become an irritation to your dog.
Uveal Eye Tumor Dog. Dog eye melanoma or uvea tumors are another common form of malignant tumors which are related to the dog eye pigment cells excluding retinal pigment cells. This type of eye tumor in dog originates from melanocytes of.
Homeopathic treatment of tumors on the eye of a dog. Heidi presented September 2000 as a 14-year-old spayed female German Shepherd with a growth on her right eye that looked red and angry local vet said cancerous It was attached to. The most common eyelid tumors in dogs are sebaceous meibomian adenomas 29 to 37 sebaceous meibomian epitheliomas 17 to 34 sebaceous meibomian hyperplasia 18 sebaceous meibomian adenocarcinomas 5 to 15 papillomas 2 to 17 melanocytomasmelanomas 2 to 21 and histiocytomas 1 to 4.
12 Note that some. Eyelid tumors in dogs. Tumors of the eyelid in dogs include palpebral tumors the most common being an adenoma in the Meibomian glands.
These are glands that are located in the eyelids and produce a sebaceous substance. These tumors can look like a little piece or pieces of cauliflower. Dog eye tumors may be either benign enveloped or malignant spreading in nature.
The exact cause of canine eye tumors are not yet known however genetic and environmental factors have been proven to be linked to the occurrence of these types of eye tumors in dogs. Adenomas are the benign form of dog eye tumors while adinocarcinomas are. Are eyelid tumors on dogs cancerous.
Eyelid tumors on dogs commonly known as eyelid cysts are common in both dogs and cats. An estimated 75 of all eyelid tumors in dogs are benign. However the remaining 25 are typically cancerous so its important to have a vet examine them.
If left untreated some eyelid tumors can become malignant. Orbital neoplasms in dogs produce exophthalmia conjunctival and eyelid swelling strabismus and exposure keratitis. The globe cannot be retropulsed.
Usually there is no pain. Because 90 of the neoplasms are malignant and 75 arise within the orbit the prognosis for longterm survival is often poor. The most frequently diagnosed tumors.
Eye tumors are likely to affect all structures of the eye. Globe eyelid conjunctiva nictitating membrane lacrimal gland cornea uvea etc. Melanomas can exceptionally spread to different parts of the eye and turn into tumors cancerous.
By generating metastases they then engage the dogs vital prognosis. Most vets will perform an enucleation a procedure in which your dogs affected eye is removed. This eye removal is performed for many reasons but some of the most common are when the tumor grows quickly the eye cant be saved the tumor is impeding the eyes sight and the tumor is causing additional issues such as bleeding.
Abnormal movement or darting of the eyes is a common symptom of a brain tumor that is affecting a dogs balance system. Paresis Hindbrain tumors can cause weakness in the limbs. Eyelid Tumors in Dogs Types of tumors.
Tumors of the eyelid are the most typical tumors of the eye associated tissues and can originate from any of the tissues of the lid. Adenomas benign tumor and adenocarcinomas gland cancer of the oil glands are the most common. Older dogs typically establish eyelid growths.
Mastocytoma mast cell tumor Papilloma benign epithelial tumor Fortunately eyelid tumors in dogs are usually benign and do not spread to distant tissues. Surgical removal cures most tumors of the eyelid but complete removal sometimes can cause eyelid deformities 1. Eyelid tumors can become quite large and be very disfiguring.
Mast cell tumors are malignant tumors that occur in the mast cells in a dogs skin. Normal mast cells are a type of immune system cell. They play a role in allergic reactions such as hives and bug bites.
Mast cell tumors may look like a. Advanced eyelid tumors may extend into the soft tissues behind the eye into the orbit or into the eye. Home Care for Dogs with Eyelid Tumors.
Optimal treatment for your dog requires a combination of home and professional veterinary care. Most dogs are sent home wearing an Elizabethan collar to prevent self-trauma to the surgery site.