
On microscopic examination neoplasms were composed of tubules. Insulinomas prevent the pancreas from functioning properly.
Generally these tumors are malignant and are most common in Airedales and Boxers.
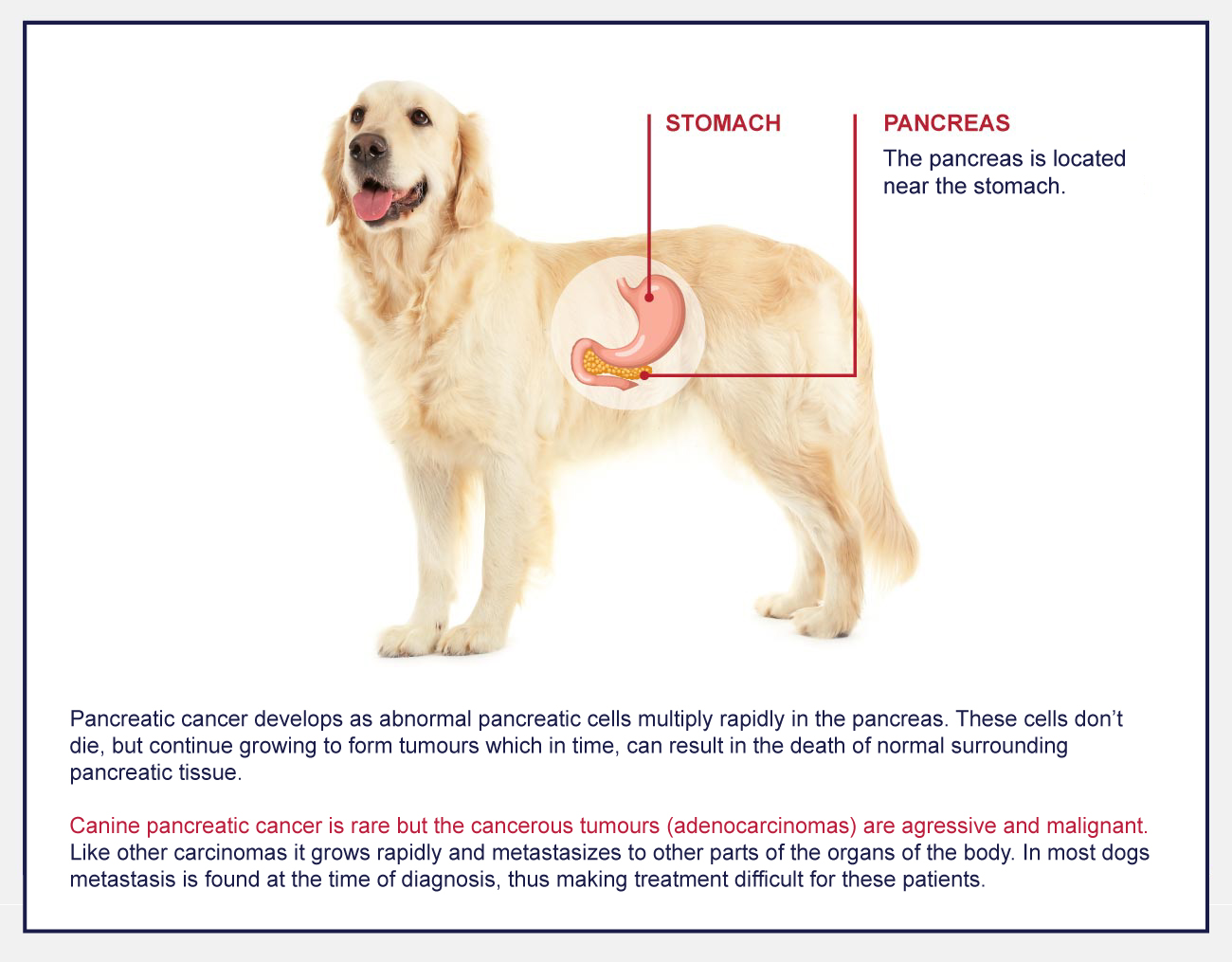
Pancreatic tumor dogs. If your dog is diagnosed as having a pancreatic tumor it means that the cells within a specific part of your pups pancreas are overproducing reproducing excessively. As with most tumors in animals and people your dogs pancreatic tumor could be either benign non-cancerous or malignant cancerous. What Is Pancreatic Cancer Adenocarcinoma In Dogs.
When dealing with a pancreatic tumor in dogs there are four main types. Adenocarcinomas insulinomas gastrinomas and glucagonomas. While they affect different types of cells within the pancreas they are all malignant tumors meaning they are cancerous and might spread to other areas of the body.
Pancreatic Cancer in Dogs The Prognosis As noted pancreatic tumors are often malignant meaning that there is a high probability that cancer has spread before its been detected. Unfortunately this can make for a poor prognosis for dogs with pancreatic cancer. If the type of tumor has been identified and your Vet completed staging tests they may be able.
Types of Pancreatic Tumors in Dogs. There are two main types of pancreatic tumors in dogsinsulinomas and adenocarcinomas. One affects the pancreas exocrine cells that produce enzymes and one affects the endocrine cells which produce insulin.
Both types of cancer typically originate in the pancreas and are typically malignant. Primary pancreatic tumors are rare in dogs and cats. Exocrine tumors include adenomas and adenocarcinomas and endocrine tumors include insulinomas gastrinomas and glucagonomas.
Insulinomas are the most common type of pancreatic tumor followed by adenocarcinomas. Both tumors are more common in dogs than cats. Large breed dogs and Siamese cats may be.
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma in Dogs A carcinoma is a type of malignant tumor found in both humans and animals and tends to be particularly malignant with recurring growth after surgical excision. Adenocarcinomas are characterized as glandular in structure andor originating in the glandular tissue. Many symptoms of pancreatic cancer in dogs are non-specific.
Therefore it is difficult to tell if a dog showing the symptoms has pancreatic cancer or other benign pancreatic disease. For example a dog with pancreatic cancer may show signs such as. Hyperglycemia elevated blood sugar.
Exocrine pancreatic carcinoma is a particularly malignant neoplasm of the dog. Clinical and pathologic findings of an unusual variant of exocrine pancreatic neoplasia termed hyalinizing pancreatic adenocarcinoma were evaluated in 6 dogs. On microscopic examination neoplasms were composed of tubules.
The biologic behaviour observed in both dogs and cats has been presumed to be akin to that of humans with only few reports describing the behaviour of exocrine pancreatic carcinomas in veterinary medicine. 3-6 These tumours were described as rare in both dogs and cats with increasing age being a predisposing risk factor. If your dog is diagnosed as having a pancreatic tumor it means that the cells within a specific part of your pups pancreas are overproducing reproducing excessively.
As with most tumors in animals and people your dogs pancreatic tumor could be either benign non-cancerous or malignant cancerous. In dogs malignant pancreatic tumors are more common than benign however both are relatively rare. The most common form of pancreatic cancer seen in dogs is insulinoma followed by adenocarcinoma.
The different forms of pancreatic cancer in dogs will produce a host of different symptoms. Exocrine pancreatic tumors are rare with a reported incidence of 178 and 126 per 100000 patient years at risk in the dog and cat respectively. 32 They are typically of epithelial origin and malignant tumors carcinoma adenocarcinoma are more common than benign adenomas.
33 Benign nodular hyperplasia is a common incidental finding in older animals which can appear. Pancreatic endocrine tumors in dogs have been most often associated with excess insulin secretion and hypglycemia A few of these tumors have also been associated with gastrin secretion and a Zollinger-Elli- son-like syndrome68. Dogs with pancreatic cancer oftentimes have a difficult time eating sufficient amounts of food.
You may notice that your pets overall appetite has diminished as a result of his tumorous growth. As this happens your pet will lose out on nourishment that he would otherwise be eating and his weight will gradually and consistently go down. An insulinoma is a tumor of the pancreas that affects the regulation of your dogs sugar levels causing hypoglycemia also referred to as low blood sugar.
This tumor usually occurs in middle-aged or older dogs. Both mixed breeds and pure breeds can be affected by this type of tumor. Some of the most common pure breeds at risk are.
Pancreatic cancer in dogs is either Primary or Secondary. Primary tumors are when the neoplasm tumor develop in the pancreas and secondary tumors are when the cancer has developed in another organ and then spread metastasized to the Pancreas. If Your Dog Has Cancer You NEED This Book.
Benign and malignant tumors in dogs. Once your dog receives a diagnosis of tumors in the pancreas the veterinarians treating your pet will compile a treatment plan that they believe is most fitting for your dogs situation. Some examples of treatment options include.
Partial or total surgical removal of pancreatic tumor Surgical removal of an entire pancreas. Insulinoma is a cancerous growth also known as a tumor located on the pancreas in dogs. A healthy pancreas helps produce insulin which controls the glucose levels in the dogs body.
Insulinomas prevent the pancreas from functioning properly. These tumors cause the insulin levels to rise dramatically which in turn cause the glucose levels to decrease. Generally these tumors are malignant and are most common in Airedales and Boxers.
Pancreatic exocrine neoplasia is an aggressive cancer that will spread to tissues that are nearby and even to the other organs throughout your dogs body. Most dogs affected with this cancer are middle-aged to senior dogs. Since these tumors often block the bile duct jaundice is another common sign.
When tumors press on veins the resulting buildup of fluid can cause abdominal swelling. In addition simultaneous leakage of digestive enzymes from the pancreas breaks down and destroys surrounding tissues increasing the dogs pain. Benign exocrine pancreatic tumors are rare.
Nodular hyperplasia hard pale elevations on the surface of the gland is common in dogs. Older breeds and spaniels are predisposed. Causes Like all other cancers the etiology of exocrine pancreatic cancer is also unknown.
But in order to study the incipient phase and growth behavior of.