The spinal cord is the part of the CNS located within the vertebral canal. Comparative Anatomy Dog Skeleton vs.
Individually the joints between vertebrae are not very mobile the movement of the upper synovial joints is very limited just a sliding movement but as a whole the spine can perform movements of flexion and extension.
Veterbrae anatomy dog. The dog spine anatomy consists of vertebrae intervertebral disc spinal cord spinal nerves and other associated structures. If you are a veterinary practitioner or student you may treat some common spinal problems of a dog. For that you might have a good piece of knowledge on the anatomy of a dog spine.
The dogs spine is divided into cervical vertebrae thoracic vertebrae lumbar vertebrae sacral vertebrae and coccygeal vertebrae. There are seven cervical vertebrae in every dog even if some dogs may have a longer neck than others. From Evans HE.
Millers anatomy of the dog ed 4 Philadelphia 2013 WB Saunders All vertebrae except the sacral vertebrae remain separate and form individual joints. Four sites with limited motion exist within the canine spine. 6 These sites occur at areas where the cranial and caudal articular surfaces are inclined in a nonparallel manner and in different.
If we now move on to the spine of the canine we find that there are 5 main regions of the vertebrae. From the head down to the neck are 7 cervical vertebrae. These vertebrae are quite flat in shape compared to the rest.
Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines eg. Muscle organ and skeletal anatomy. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds.
Atlas of anatomy on x-ray images of the dog. This module of vet-Anatomy is a basic atlas of normal imaging anatomy of the dog on radiographs. 51 sampled x-ray images of healthy dogs performed by Susanne AEB Borofka PhD - dipl.
ECVDI Utrecht Netherland were categorized topographically into seven chapters head vertebral column thoracic limb pelvic. Comparative Anatomy Dog Skeleton vs. Discuss the bones of the animal skull.
Figure 6-10 Page 165 Usually consists of 37 or 38 separate. Vertebrae Anatomy Review. Figure 6-16 Page 170 Vertebral foramina line up to form the spinal canal.
It consists of sensory and sympathetic postganglionic fibers that innervate the dura mater the dorsal longitudinal ligament the vertebral venous sinuses and other vessels located in the vertebral canal Page 832 of Millers anatomy of the dog by Evans HE. The dog has 321 bones. Regions of a Long Bone Structure of a Long Bone articular cartilage nutrient artery entering nutrient foramen marrow cavity compact bone spongy bone ligament periosteum endosteum physis epiphyseal plate physis epiphyseal plate metaphysis diaphysis metaphysis epiphysis epiphysis.
Canine Muscle Origins Insertions Actions and Nerve Innervations The purpose of this document is to provide students of canine anatomy a simple reference for muscular origins insertions actions and nerve innervations without having to search through the overwhelming verbiage that accompanies most canine anatomy texts. This is an online quiz called Canine Vertebrae. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper.
Paired strap muscle which takes origin from the caudal vertebrae loops around the anus and travels along the ventral aspect of the penis and insert at the level of the preputial fornix. What does it do. Contraction of this muscle maintains the position of the non-erect penis within the prepuce.
The prevalence of lumbosacral transitional vertebrae LTV was determined by reviewing the pelvic radiographs of 4000 medium- and large-breed dogs of 144 breeds routinely screened for canine hip dysplasia. An LTV was seen in 138 35 dogs. The prevalence was higher in German Shepherd dogs and Grea.
Computed tomographic anatomy of the canine cervical vertebral venous system. Computed tomographic CT venography of the cervical vertebral canal was performed in six clinically normal adult mixed-breed dogs from 14 to 23 kg. After dogs were euthanized and saline perfused a gelatin and iothalamate mixture was injected into the right external.
Anatomy of the canine lumbar vertebrae and lumbosacral junction CT This anatomical module of the atlas of veterinary radiological anatomy vet-Anatomy covers the lumbar vertebrae lumbosacral joint sacrum and caudal vertebrae of the dog on a Computed Tomography CT and on 3D images of the lumbar spine and pelvic girdle. The spinal cord is the part of the CNS located within the vertebral canal. It is involved in controlling movements of the trunk and limbs regulates visceral functions and transmits information to and from the brain.
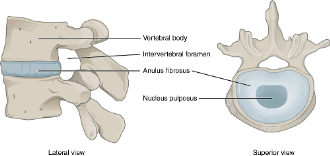
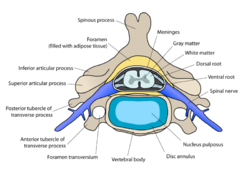
It extends from the foramen magnum in the occipital bone to the sixth or seventh lumbar vertebra in dogs. Vertebrae consist of a body which encloses the vertebral foramen through which the spinal cord and meninges run a spinous process and a transverse process as well as articular processes by which they join together. The form of the spinous process varies with respect to species and region.
Individually the joints between vertebrae are not very mobile the movement of the upper synovial joints is very limited just a sliding movement but as a whole the spine can perform movements of flexion and extension. Intervertebral joints in dogs are like those of humans. Vertebrae are the bones of the spine.
The canine spine is divided into five regions. Cervical thoracic lumbar sacral and caudal. There are 7 cervical vertebrae 13 thoracic vertebrae 7 lumbar vertebrae and 3 sacral vertebrae.
The number of caudal vertebrae varies according to the species. Cervical vertebrae edit edit source The atlas and axis are cervical vertebrae 1 and 2. THE DOGS ANATOMY Canadian Kennel Club Official Breed Standards 306-16-05 Muzzle VERTEBRAL COLUMN BACK Withers 9 Vertebrae LUMBAR 7 Vertebrae Loin Skull FEMUR Thigh PATELLA Knee Cap STIFLE Knee Joint RIBCAGE CHEST BODY Trunk FIBULA Tibia Leg.
Lower Leg TARSUS - HOCK Heel on Ankle Joint METATARSUS Rear Pastern PAWS TOES. The vertebral extremity of the dog ribs possesses a round head a distinct neck and a tubercle. In the head of the dog ribs you will find the cranial and caudal articular facets.
These facets articulate with the socket that forms by the cranial and caudal costal fovea on the bodies of the two adjacent vertebrae. The digestive system cat dog includes the mouth teeth salivary glands esophagus stomach intestine pancreas liver and gall bladder. The digestive system absorbs and digests food and eliminates solid wastes from the body.
The integumentary system is the skin and fur that cover the animals body. The skin protects the underlying organs.